Side Effects of Immunotherapy vs. Chemotherapy: A Comparative Analysis
Cancer treatment has witnessed significant advancements over the years, with a multitude of therapeutic options now available to patients. Among these, chemotherapy and immunotherapy have emerged as two primary modalities.
While both have proven effective in combating cancer, each form of cancer treatment is associated with distinct side effects. This article aims to delve into a comparative analysis of these side effects, with a particular emphasis on targeted immunotherapies like Immunocine’s Dendritic Cells.
Chemotherapy Side Effects: A Double-Edged Sword
Chemotherapy, a conventional form of cancer treatment, operates on the principle of targeting rapidly dividing cells, a characteristic feature of cancer cells. However, this non-discriminatory approach also impacts healthy cells that exhibit rapid division, leading to a range of side effects.
According to a study by Rani Lisa Indra and Bayu Saputra, patients undergoing chemotherapy reported nausea, weakness, hair loss, vomiting, loss of appetite, and weight loss as the most disturbing physical side effects. These side effects are not just transient but persist throughout the chemotherapy regimen, as highlighted by a study conducted by A. Pearce et al.
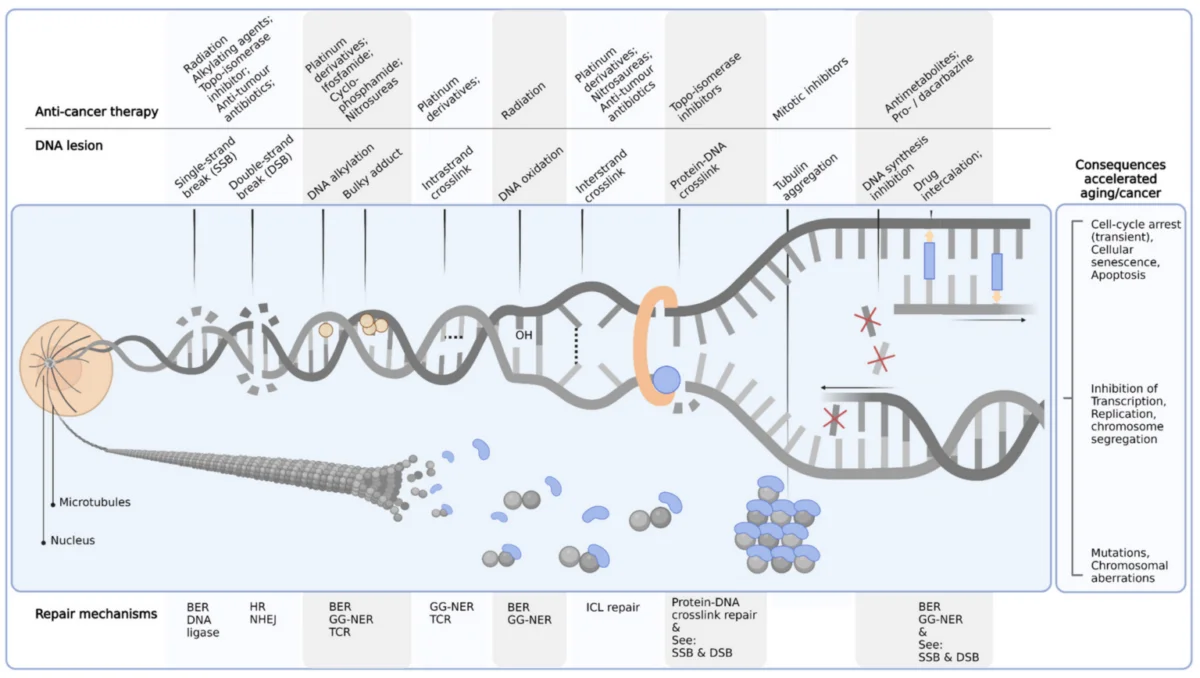
Moreover, chemotherapy can lead to DNA damage, which can result in varying toxicities and accelerate features of aging, depending on the type and dose of chemotherapeutic, clearing method, and the organ affected. This was discussed in a paper by W. M. C. van den Boogaard et al.
Immunotherapy Side Effects: Harnessing the Body’s Defenses
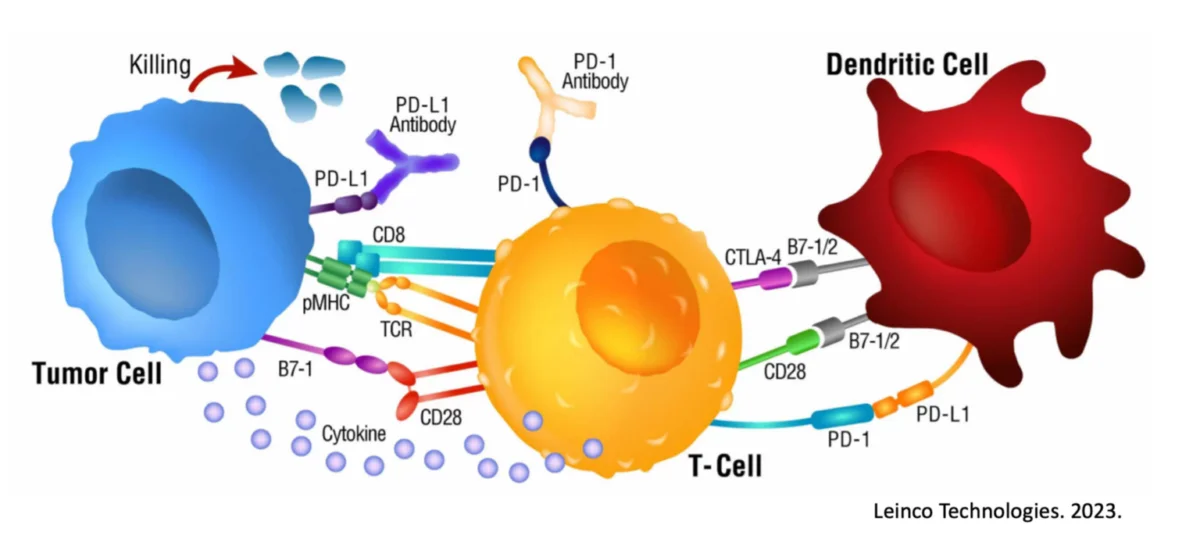
Immunotherapy, in contrast, leverages the body’s immune system to combat cancer. It includes treatments like targeted therapies that specifically focus on cancer cells, thereby minimizing damage to healthy cells. A key player in this field is Immunocine’s Dendritic Cells.
According to a paper by B. Kong et al., combining dendritic cell-based immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors can enhance the immune response to tumor antigens while reducing tumor-associated immune inhibitory mechanisms. This strategy maximizes specific immune responses and promotes long-lasting immunological memory.
However, immunotherapy is not devoid of side effects. These are often symptoms of an aggressive immune response, akin to how the body reacts when it is unwell. For instance, a study by Evgeniia Korotchenko et al. found that allergen-polysaccharide neoglycoconjugates can increase the efficacy of immunization by targeting and activating dendritic cells, while reducing side effects.
Conclusion
While both chemotherapy and immunotherapy present their own set of side effects, it’s crucial to remember that these treatments are not mutually exclusive and can often be used in combination to enhance efficacy. The choice between chemotherapy and immunotherapy, or a combination of both, should be made based on the individual patient’s condition, type of cancer, and personal preferences.
In conclusion, the landscape of cancer treatment is complex and rapidly evolving. As we continue to understand the intricacies of these therapies and their side effects, the ultimate goal remains to improve patient outcomes and quality of life. Always consult with your healthcare provider to understand the best treatment options for you.
References
1. Indra, R. L., & Saputra, B. (2021). PERCEPTION OF CANCER PATIENTS ON CHEMOTHERAPY SIDE EFFECTS. Jurnal Riset Kesehatan, 10(1), 1-6.
2. Pearce, A., Haas, M., Viney, R., Pearson, S., Haywood, P., Brown, C., & Ward, R. (2017). Incidence and severity of self-reported chemotherapy side effects in routine care: A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE, 12(10), e0184360.
3. van den Boogaard, W. M. C., Komninos, D., & Vermeij, W. (2022). Chemotherapy Side-Effects: Not All DNA Damage Is Equal. Cancers, 14(3), 627.
4. Kong, B., Liu, G. B., Zhang, J. A., Fu, X. X., Xiang, W. Y., Gao, Y., & Xu, W. S. (2019). On the Other Side: Manipulating the Immune Checkpoint Landscape of Dendritic Cells to Enhance Cancer Immunotherapy. Frontiers in Oncology, 9, 50.
5. Korotchenko, E., Dewes, J., Waschke, J., & Peschel, A. (2020). Laser‐facilitated epicutaneous immunotherapy with hypoallergenic beta‐glucan neoglycoconjugates suppresses lung inflammation and avoids local side effects in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Allergy, 75(11), 2895-2905.
READ THIS NEXT
Dr. Nasha Winters’ Mission to Create a New Standard of Cancer Treatment
For decades, Dr. Nasha Winters has been a dynamic force in the field of integrative oncology with an emphasis on the metabolic approach to c
Read MoreWhy Cancer May Stop Responding to Treatment — The Importance of Adaptive Cancer Therapies
Cancer is a complex and challenging disease to treat. While many cancers initially respond well to treatment, it’s not uncommon for th
Read MoreThe Unsung Heroes: Dendritic Cells in the Battle Against Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer stands as one of the most formidable adversaries in the realm of oncology. This silent killer often evades early detection
Read More